Depreciation in Income Tax
Meaning of Depreciation
It refers to a decrease in the value of assets by wear and tear, caused by their use in the business over a period of time. Its cost is spread over its anticipated life by charging depreciation every year against the profits of the business.
Conditions for allowance of depreciation.
- The asset must be owned by the assesse.
- It must be used for the purpose of business or profession.
- It must be used in the relevant accounting year.
Assets eligible for depreciation
A. Tangible Assets: Buildings, Machinery, Plant and furniture
B. Intangible Assets: Know-how, Patents, Copyrights, Trademarks, Licences, Franchises or any other commercial rights of similar nature.
Buildings means only superstructure and does not include the land on which it is constructed.
Plants includes ships, vehicles, books, scientific apparatus and surgical equipment used for the purpose of business or profession. It does not include animals, tea bushes, buildings, furniture or fittings.
It means group of assets falling within a class of assets comprising Tangible and Intangible assets. In Income Tax, depreciation is calculated on the block of assets instead of individual assets.
In the case of undertakings engaged in generation and distribution of power – depreciation may be claimed on the basis of Straight Line Method. In any other case Written Down Value is followed.
If the asset is acquired and is used in the business for less than 180 days in the previous year, only 50% of the normal depreciation will be allowed. This provision is applicable in both Straight line and Written Down Value method.
The amount of depreciation shall be deducted in computing income, whether or not the assessee has claimed the deduction in respect of depreciation.
If a motar car manufactured outside India is acquired after 31st March 2001 and used for building or profession of the assessee in India, depreciation is allowed on such car with effect from the AY 2002-2003.
No depreciation is allowable in respect of building taken on lease or rent and used for the purposes of his business as the assessee is not the owner of such building.
Additional Depreciation on Plant or Machinery
As per Section 32(1)(iia) of the Income Tax Act, 1961 in case of new plant or machinery (other than ships and aircraft) acquired and installed after 31st March 2005 by an assessee engaged in the manufacture or production of any article or things or in a business of generation, transmission or distribution of power, additional depreciation at 20% (10% if the asset is put to use for less than 180 days) of actual cost of such machinery or plant will be allowed as deduction.
a) any plant or machinery purchased before 1-4-05 but installed after 31-3-05;
b) any plant or machinery, which before its installation was used within or outside India; or
c) any machinery or plant installed in office premises or any residential accommodation including guest house;
d) any office appliances or road transport vehicles, ships and aircrafts
e) any machinery or plant the whole of the actual cost of which is allowed as a deduction as depreciation or otherwise.
f) building or furniture even if the other conditions are satisfied.
g) Computers installed in office. However, if the office premises are used as industrial premises and the computers installed are used for carrying out operations of data processing, system designing. software development and supply or for supervising manufacturing activity, the such computers are eligible for additional depreciation.
Additional depreciation allowed will be deducted from WDV of the asset.
Written Down Value (WDV)
It means the actual value of the asset to the assessee, if it is acquired in the previous year. If the asset is acquired before the previous year, the actual cost less depreciation actually allowed to him. The amount of unabsorbed depreciation c/f is treated as ‘depreciation actually allowed’. If the income of an assessee derived partly from agriculture or partly from business, the WDV of asset acquired before the PY will be calculated as if it is derived from business.
Computation of WDV of Block of Assets
Simplified view
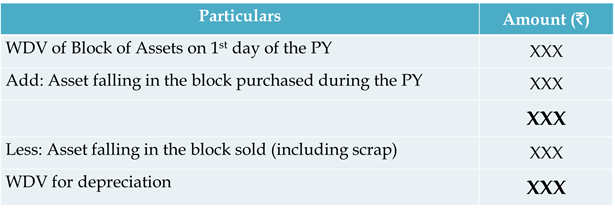 |
| Computation of WDV of Block of Assets |
Rates of Depreciation on Written Down Value Method
Do Not Write below this note
=====================================
Redrafted for Educational Purpose.
Deekshith Kumar,
Assistant Professor of Commerce
Book Reference:
1. Income Tax Law and Accounts, by Dr. H. C. Mehrotra and Dr. S. P. Goyal
2. Business Taxation by Sadashiva Rao

Comments
Post a Comment